Note
Click here to download the full example code
Sampling in dimension D
We discuss the performances of several Monte Carlo samplers on a toy example in dimension 5.
Introduction
First of all, some standard imports.
import numpy as np
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams.update({"figure.max_open_warning": 0})
use_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
dtype = torch.cuda.FloatTensor if use_cuda else torch.FloatTensor
Our sampling space:
from monaco.euclidean import EuclideanSpace
D = 8
space = EuclideanSpace(dimension=D, dtype=dtype)
Our toy target distribution:
from monaco.euclidean import GaussianMixture, UnitPotential
import math
N, M = (10000 if use_cuda else 50), 2
Nlucky = 100 if use_cuda else 2
nruns = 10
niter = 100
test_case = "gaussians"
if test_case == "gaussians":
# Let's generate a blend of peaky Gaussians, in the unit square:
m = torch.rand(M, D).type(dtype) # mean
s = torch.rand(M).type(dtype) # deviation
w = torch.rand(M).type(dtype) # weights
m[0, :] = (1.0 / (2 * math.sqrt(D))) * torch.ones(D).type(dtype)
m[0, 0] = -m[0, 0]
m[1, :] = -(1.0 / (2 * math.sqrt(D))) * torch.ones(D).type(dtype)
m[1, 0] = -m[1, 0]
m += 1
s = math.sqrt(0.4 / D) * torch.ones(M).type(dtype)
m /= 2
s /= 2
w = torch.ones(M).type(dtype)
w = w / w.sum() # normalize weights
distribution = GaussianMixture(space, m, s, w)
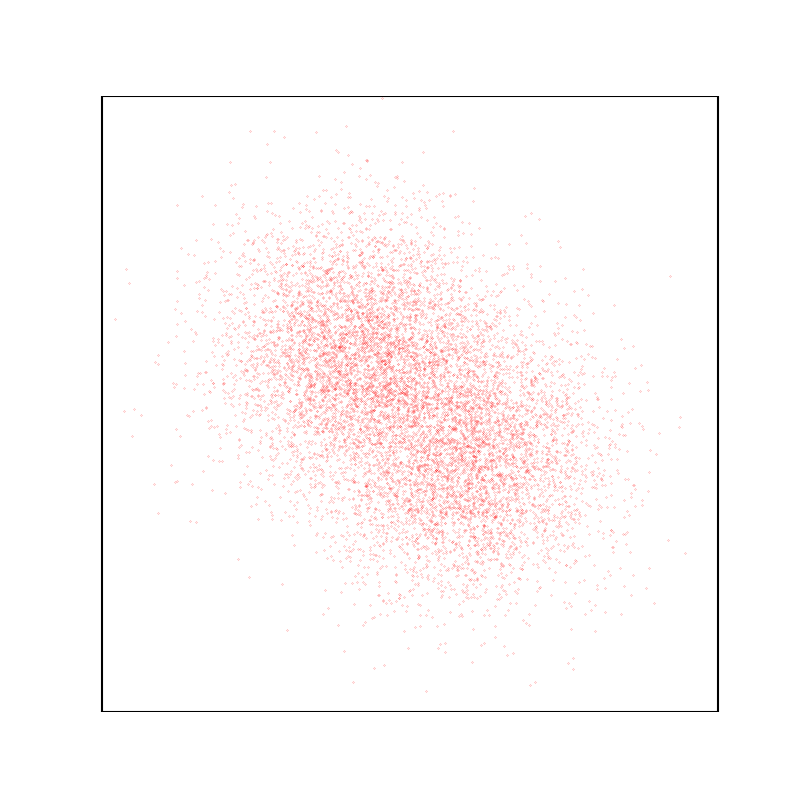
Display the target density, with a typical sample.
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
space.scatter(distribution.sample(N), "red")
space.plot(distribution.potential, "red")
space.draw_frame()
Sampling
We start from a uniform sample in the corner of the unit hyper-cube:
start = 0.9 + 0.1 * torch.rand(N, D).type(dtype)
For exploration, we generate a fraction of our samples using a simple uniform distribution.
from monaco.euclidean import UniformProposal
exploration = None
exploration_proposal = UniformProposal(space)
annealing = None
Our proposal will stay the same throughout the experiments: a uniform sample on a balls with radius 0.2.
from monaco.euclidean import BallProposal
scale = 0.2
proposal = BallProposal(
space,
scale=scale,
exploration=exploration,
exploration_proposal=exploration_proposal,
)
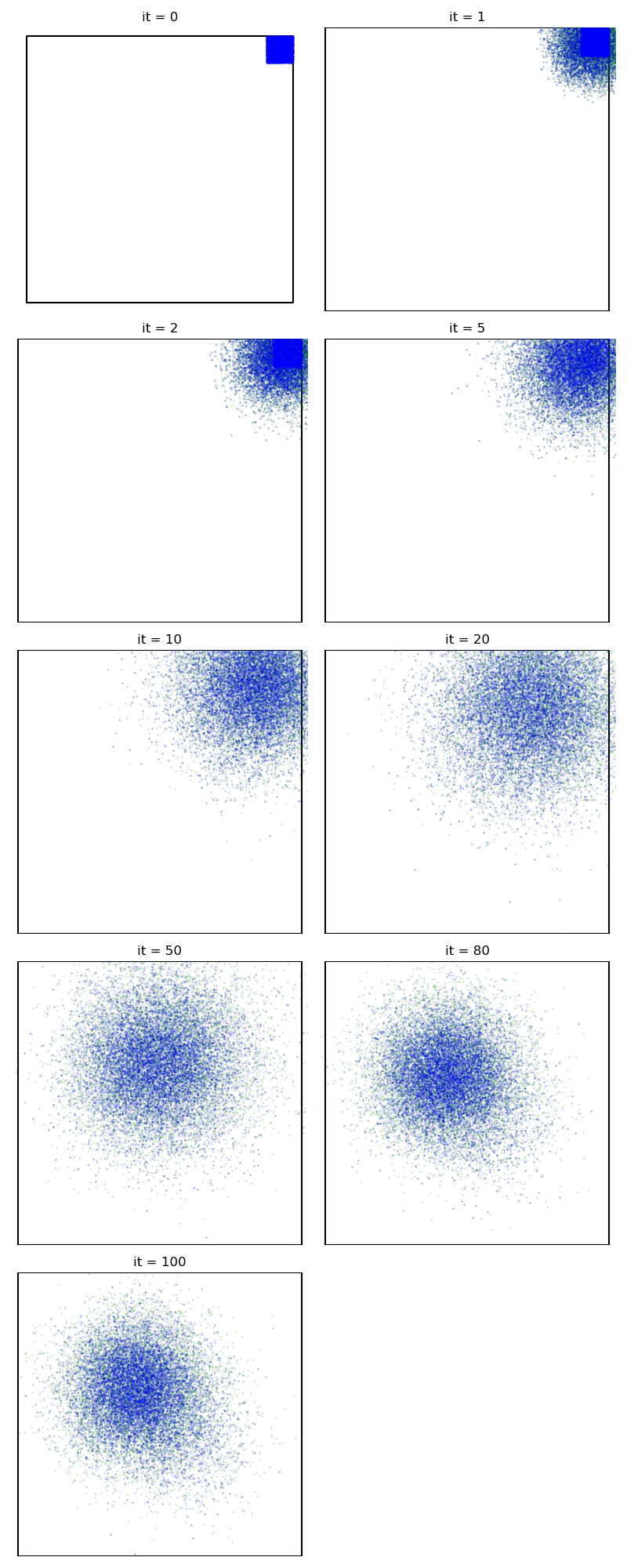
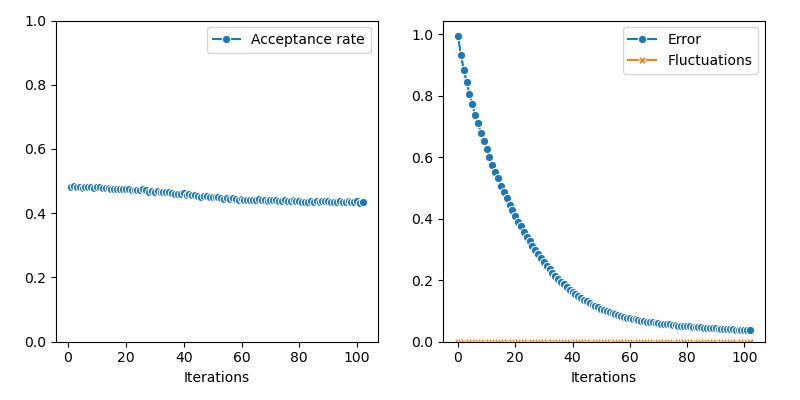
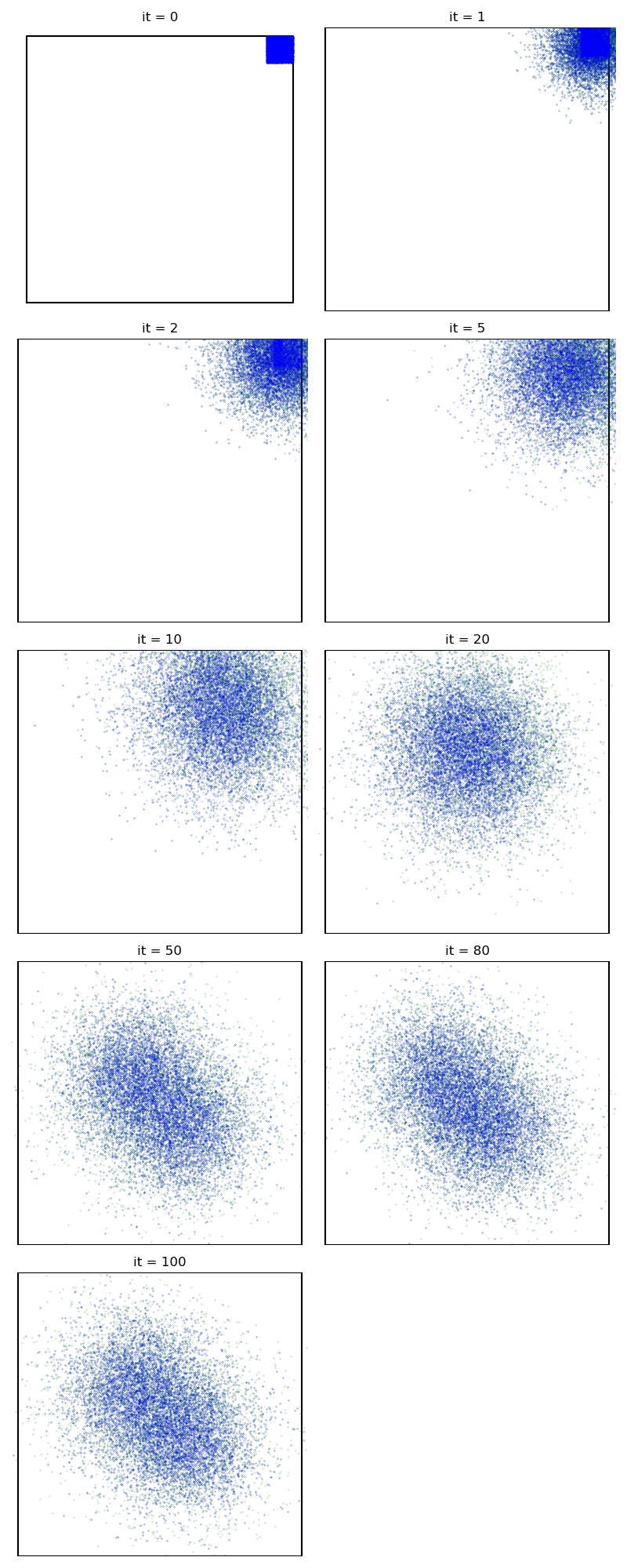
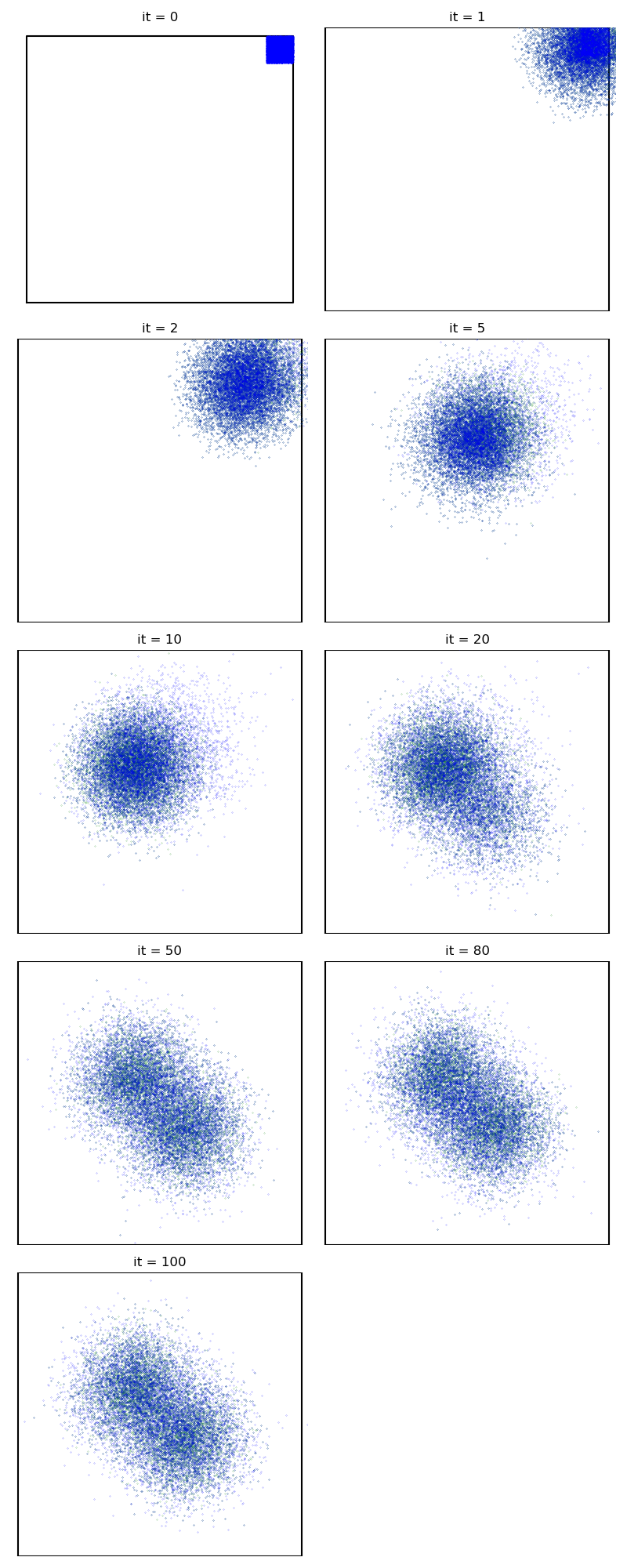
First of all, we illustrate a run of the standard Metropolis-Hastings algorithm, parallelized on the GPU:
from monaco.samplers import display_samples
info = {}
from monaco.samplers import ParallelMetropolisHastings
pmh_sampler = ParallelMetropolisHastings(
space, start, proposal, annealing=annealing
).fit(distribution)
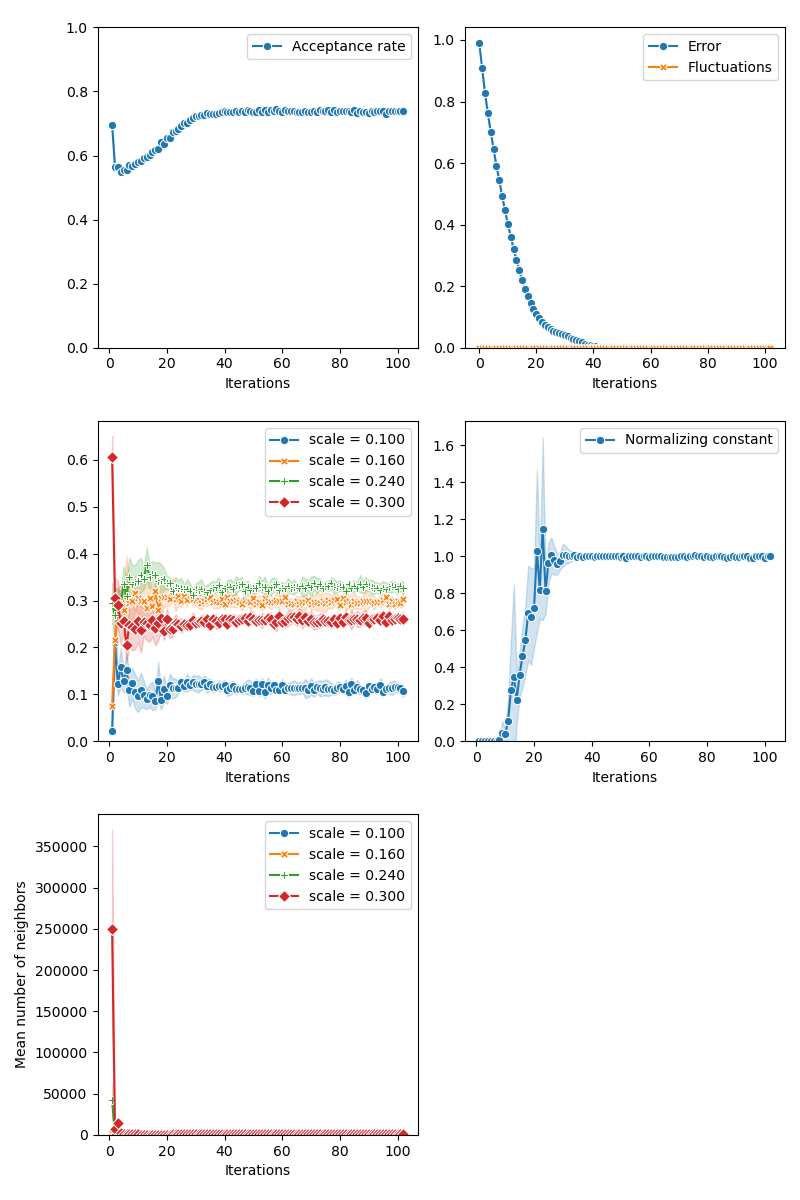
info["PMH"] = display_samples(pmh_sampler, iterations=niter, runs=nruns)
Out:
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1582: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'rocket' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name, _cmap)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1583: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'rocket_r' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name + "_r", _cmap_r)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1582: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'mako' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name, _cmap)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1583: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'mako_r' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name + "_r", _cmap_r)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1582: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'icefire' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name, _cmap)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1583: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'icefire_r' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name + "_r", _cmap_r)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1582: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'vlag' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name, _cmap)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1583: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'vlag_r' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name + "_r", _cmap_r)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1582: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'flare' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name, _cmap)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1583: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'flare_r' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name + "_r", _cmap_r)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1582: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'crest' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name, _cmap)
/home/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/seaborn/cm.py:1583: UserWarning: Trying to register the cmap 'crest_r' which already exists.
mpl_cm.register_cmap(_name + "_r", _cmap_r)
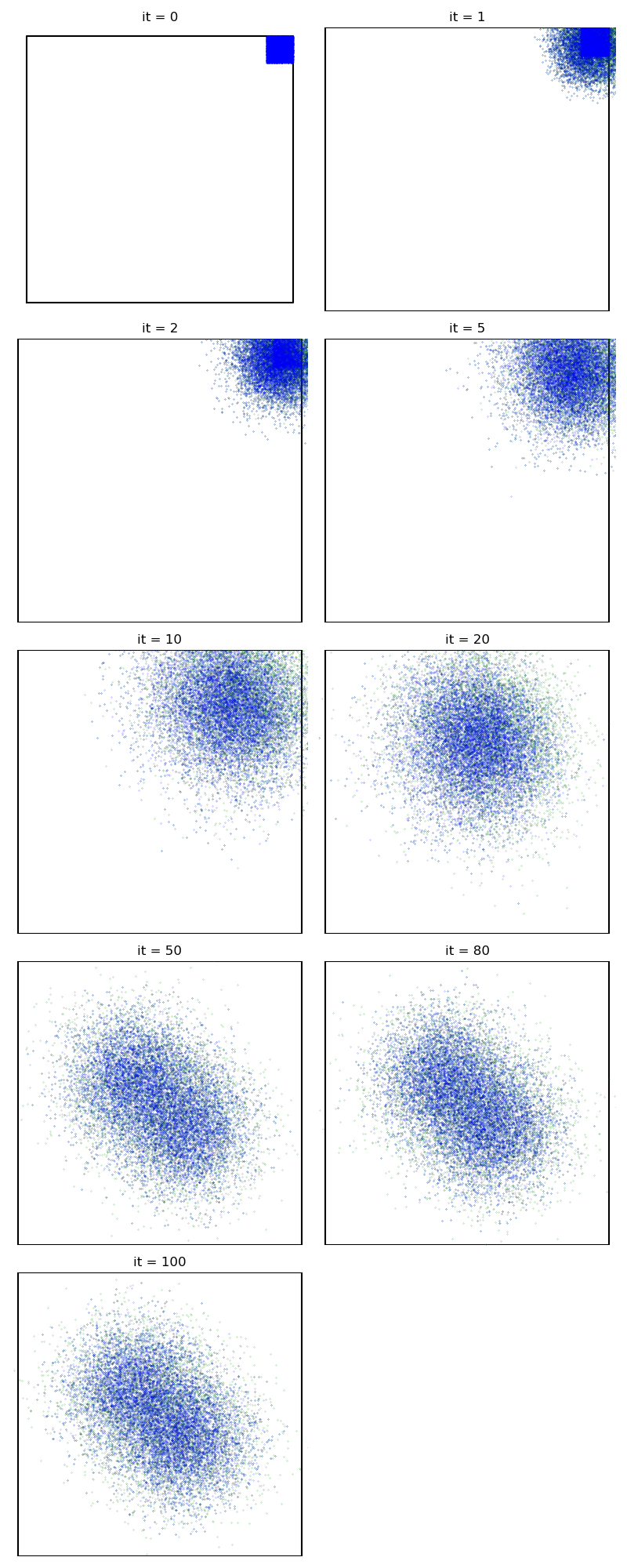
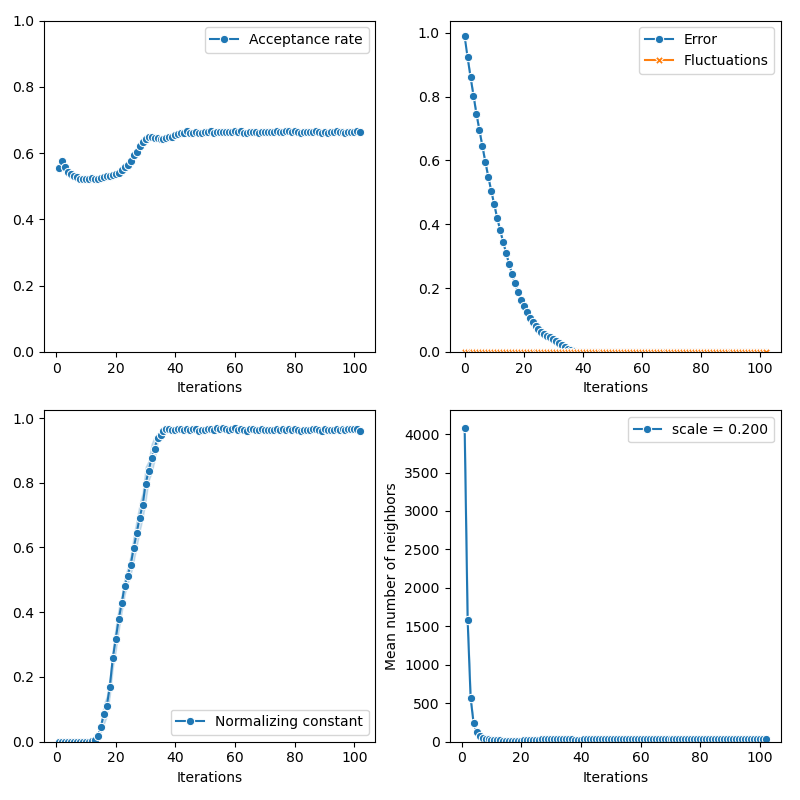
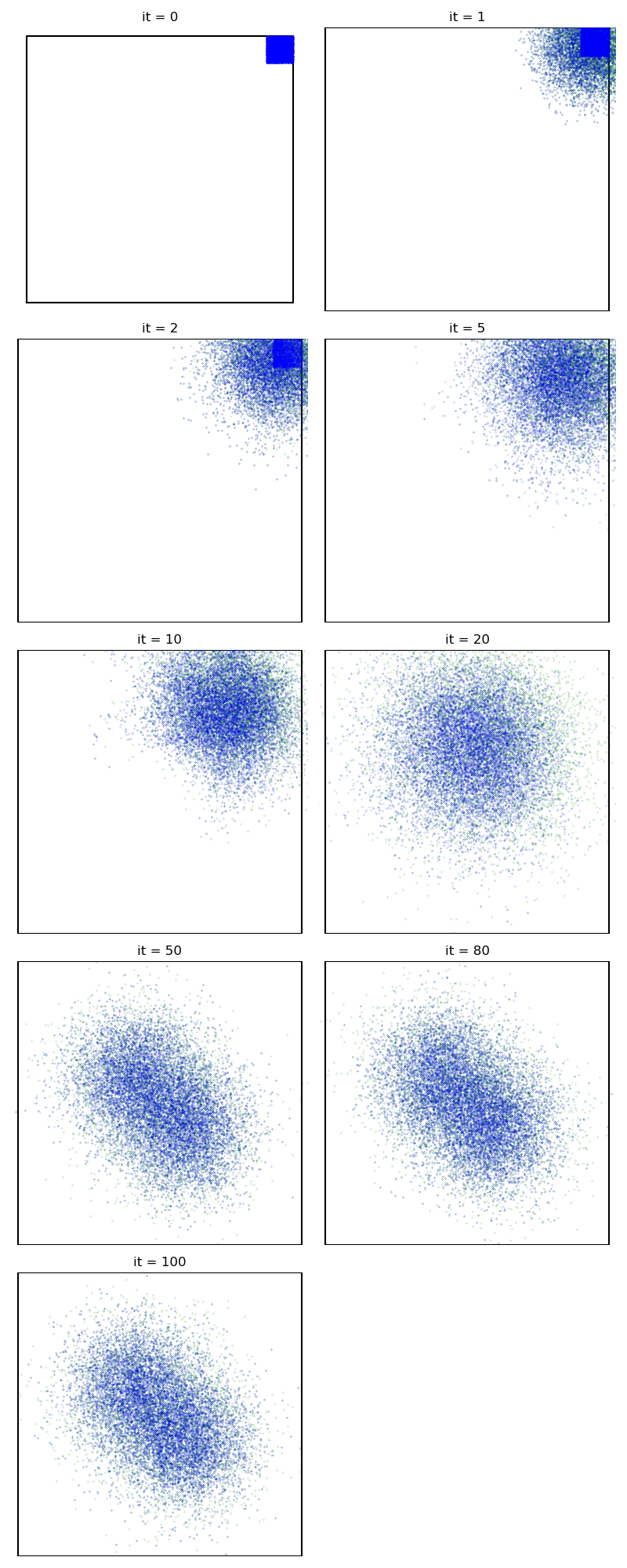
Then, the standard Collective Monte Carlo method:
from monaco.samplers import CMC
proposal = BallProposal(
space,
scale=scale,
exploration=exploration,
exploration_proposal=exploration_proposal,
)
cmc_sampler = CMC(space, start, proposal, annealing=None).fit(distribution)
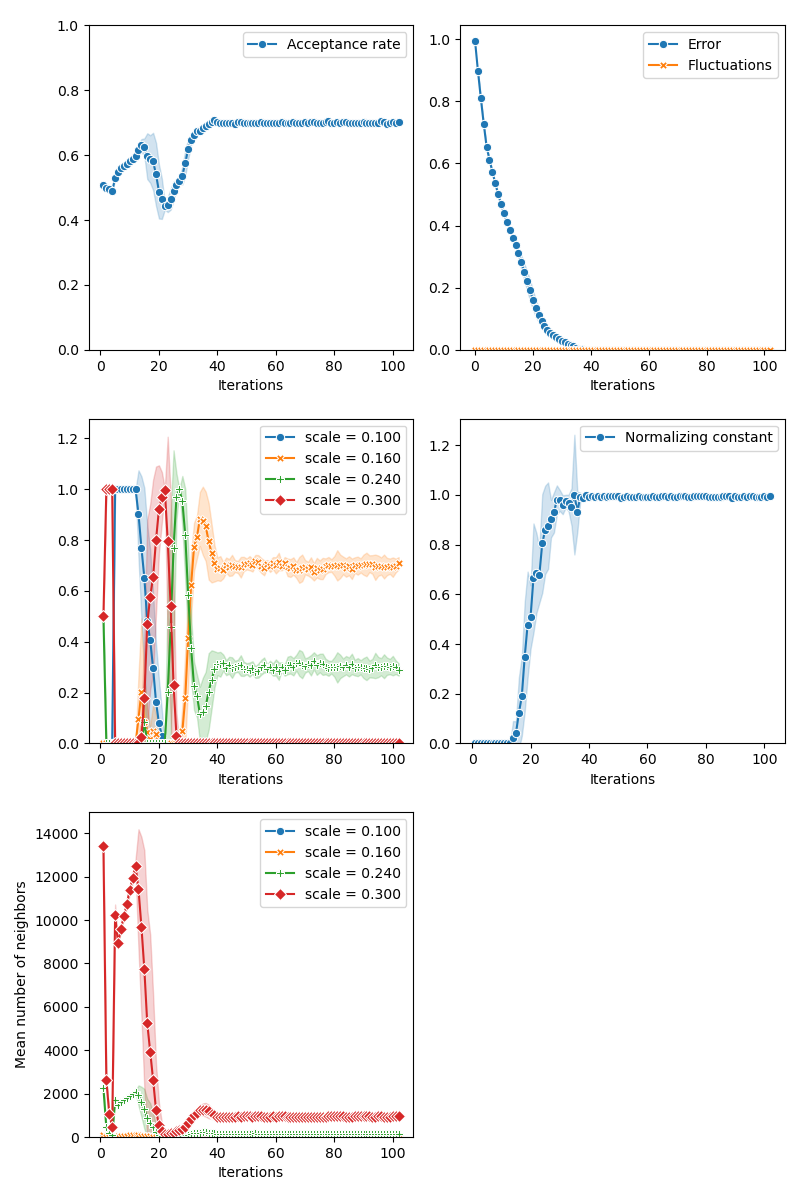
info["CMC"] = display_samples(cmc_sampler, iterations=niter, runs=nruns)
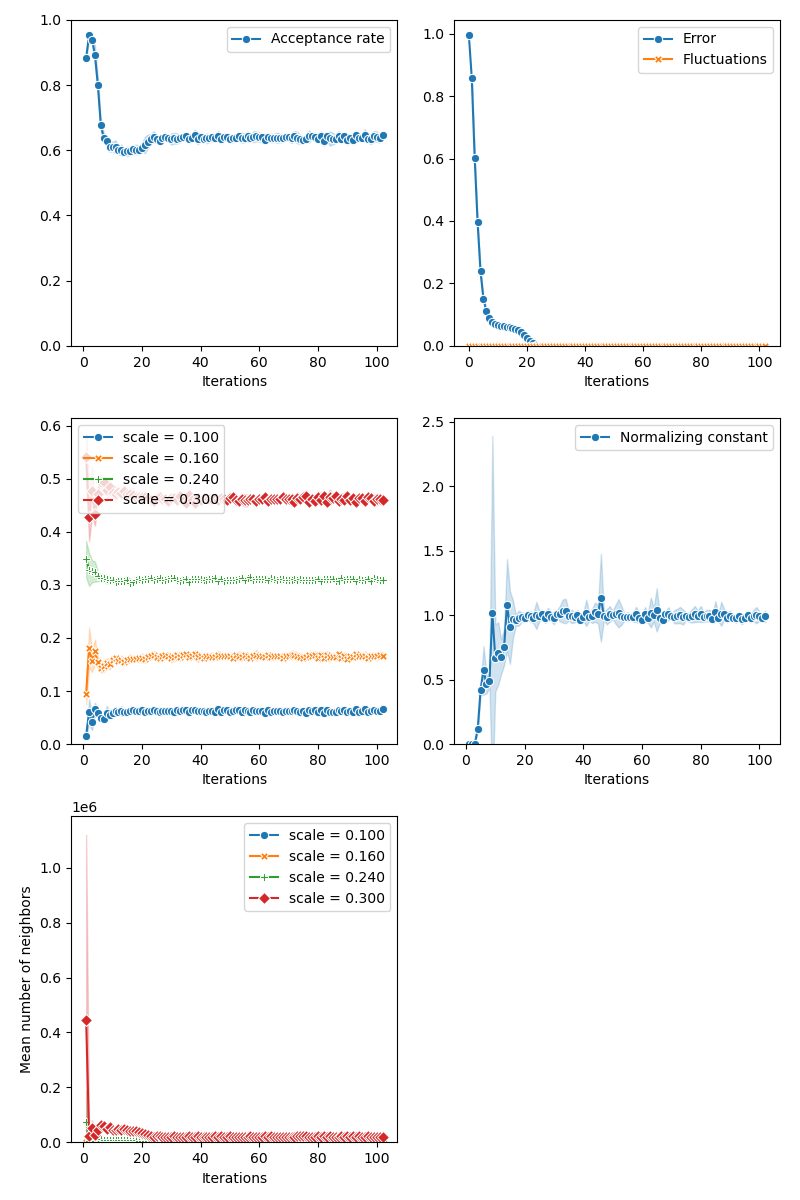
Our first algorithm - CMC with adaptive selection of the kernel bandwidth:
from monaco.samplers import MOKA_CMC
multi_scale = [0.1, 0.16, 0.24, 0.3]
proposal = BallProposal(
space,
scale=multi_scale,
exploration=exploration,
exploration_proposal=exploration_proposal,
)
moka_sampler = MOKA_CMC(space, start, proposal, annealing=annealing).fit(distribution)
info["MOKA"] = display_samples(moka_sampler, iterations=niter, runs=nruns)
With a Markovian selection of the kernel bandwidth:
from monaco.samplers import MOKA_Markov_CMC
proposal = BallProposal(
space,
scale=multi_scale,
exploration=exploration,
exploration_proposal=exploration_proposal,
)
moka_markov_sampler = MOKA_Markov_CMC(space, start, proposal, annealing=annealing).fit(
distribution
)
info["MOKA Markov"] = display_samples(moka_markov_sampler, iterations=niter, runs=nruns)
Combining bandwith estimation and deconvolution with the Moka-Kids-CMC sampler:
from monaco.samplers import MOKA_KIDS_CMC
proposal = BallProposal(
space,
scale=multi_scale,
exploration=exploration,
exploration_proposal=exploration_proposal,
)
moka_kids_sampler = MOKA_KIDS_CMC(
space, start, proposal, annealing=annealing, iterations=50
).fit(distribution)
info["MOKA_KIDS"] = display_samples(moka_kids_sampler, iterations=niter, runs=nruns)
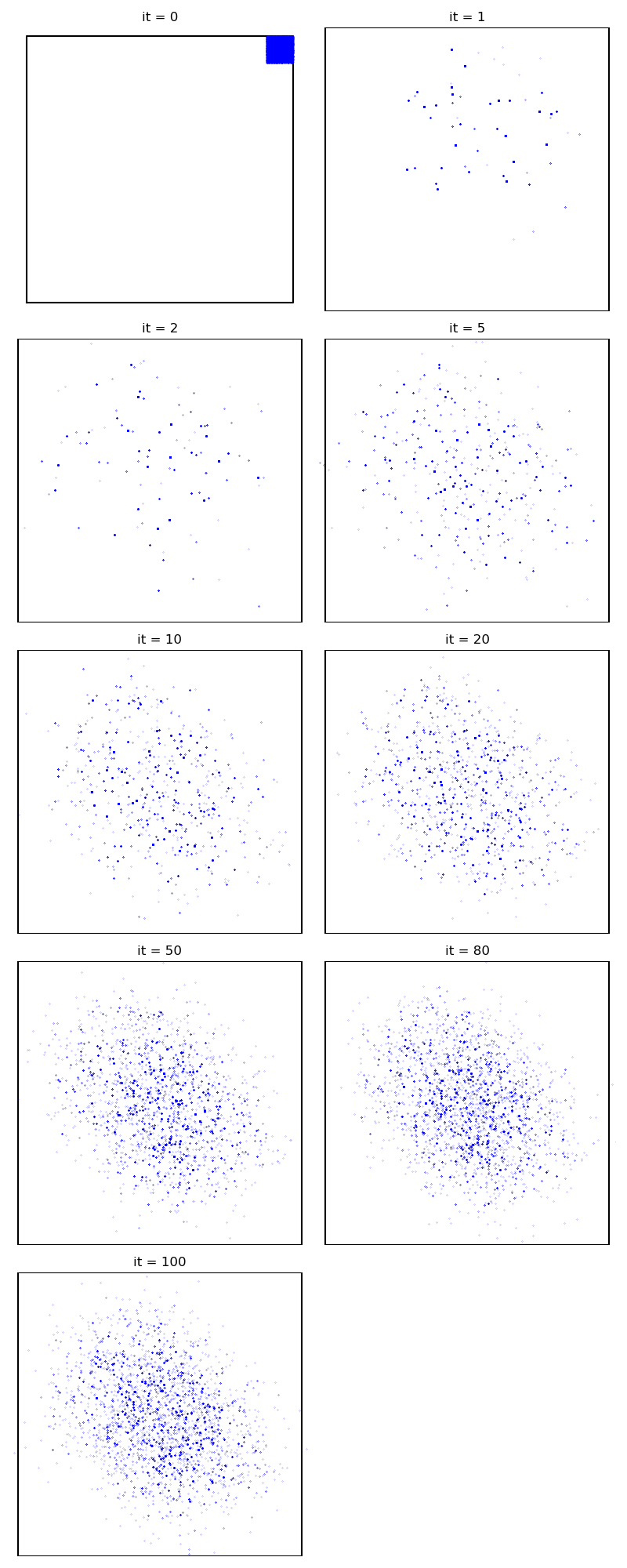
Finally, the Non Parametric Adaptive Importance Sampler, an efficient non-Markovian method with an extensive memory usage:
from monaco.samplers import SAIS
import pickle
nruns = 1
proposal = BallProposal(
space, scale=0.2, exploration=exploration, exploration_proposal=exploration_proposal
)
class Q_0(object):
def __init__(self):
None
def sample(self, n):
return 0.9 + 0.1 * torch.rand(n, D).type(dtype)
def potential(self, x):
v = 100000 * torch.ones(len(x), 1).type_as(x)
v[(x - 0.95).abs().max(1)[0] < 0.05] = -np.log(1 / 0.1)
return v.view(-1)
q0 = Q_0()
sais_sampler = SAIS(space, start, proposal, annealing=annealing, q0=q0, N=N).fit(
distribution
)
info["SAIS"] = display_samples(sais_sampler, iterations=niter, runs=nruns)
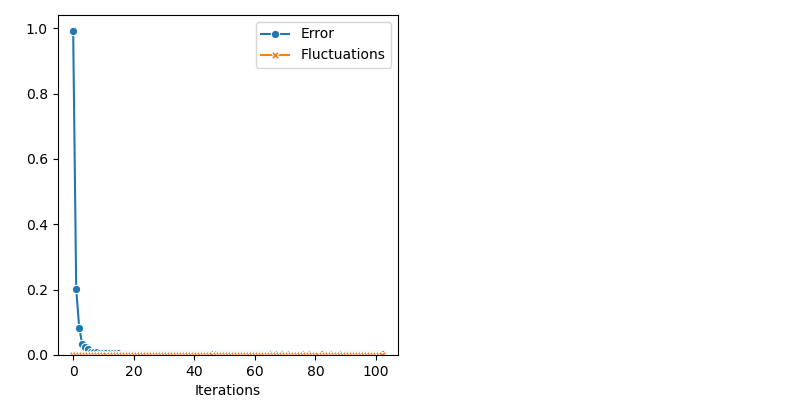
import itertools
import seaborn as sns
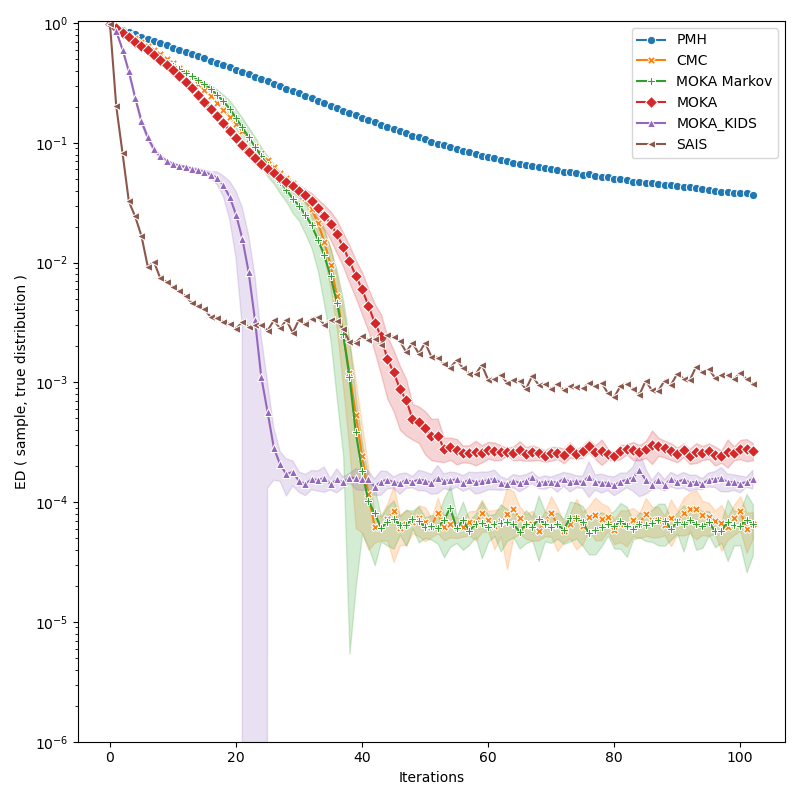
iters = info["PMH"]["iteration"]
def display_line(key, marker):
sns.lineplot(
x=info[key]["iteration"],
y=info[key]["error"],
label=key,
marker=marker,
markersize=6,
ci="sd",
)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 8))
markers = itertools.cycle(("o", "X", "P", "D", "^", "<", "v", ">", "*"))
for key, marker in zip(
["PMH", "CMC", "MOKA Markov", "MOKA", "MOKA_KIDS", "SAIS"], markers
):
display_line(key, marker)
plt.xlabel("Iterations")
plt.ylabel("ED ( sample, true distribution )")
plt.ylim(bottom=1e-6)
plt.yscale("log")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 4 minutes 44.050 seconds)